Sup. Material: The analysis of genomic features and evolutionary history of Pithovirus-like isolates reveals the existence of two major divergent groups of viruses
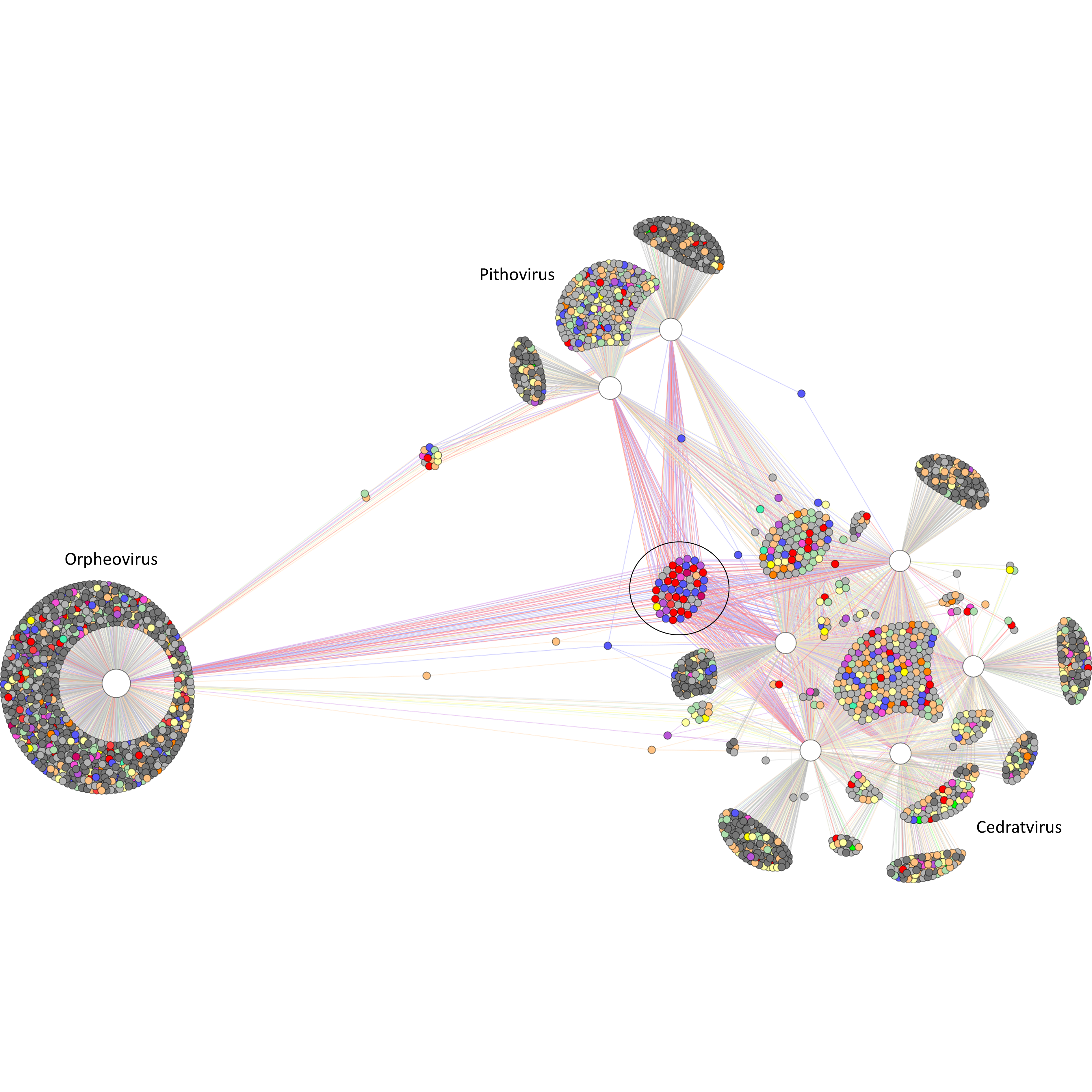
Supplementary figure 1 (above). COG sharing among the Pithovirus-like group. A bipartite network graph connects the 2586 COGs to the 8 viruses included in the pangenome analysis. Larger and white nodes correspond to the viruses. Smaller nodes correspond to the COGs, and colors refer to different functional categories, as indicated in the legend of Figure 4. The 52 COGs that compose the core genome are circulated. The graph was generated using a force-based algorithm.
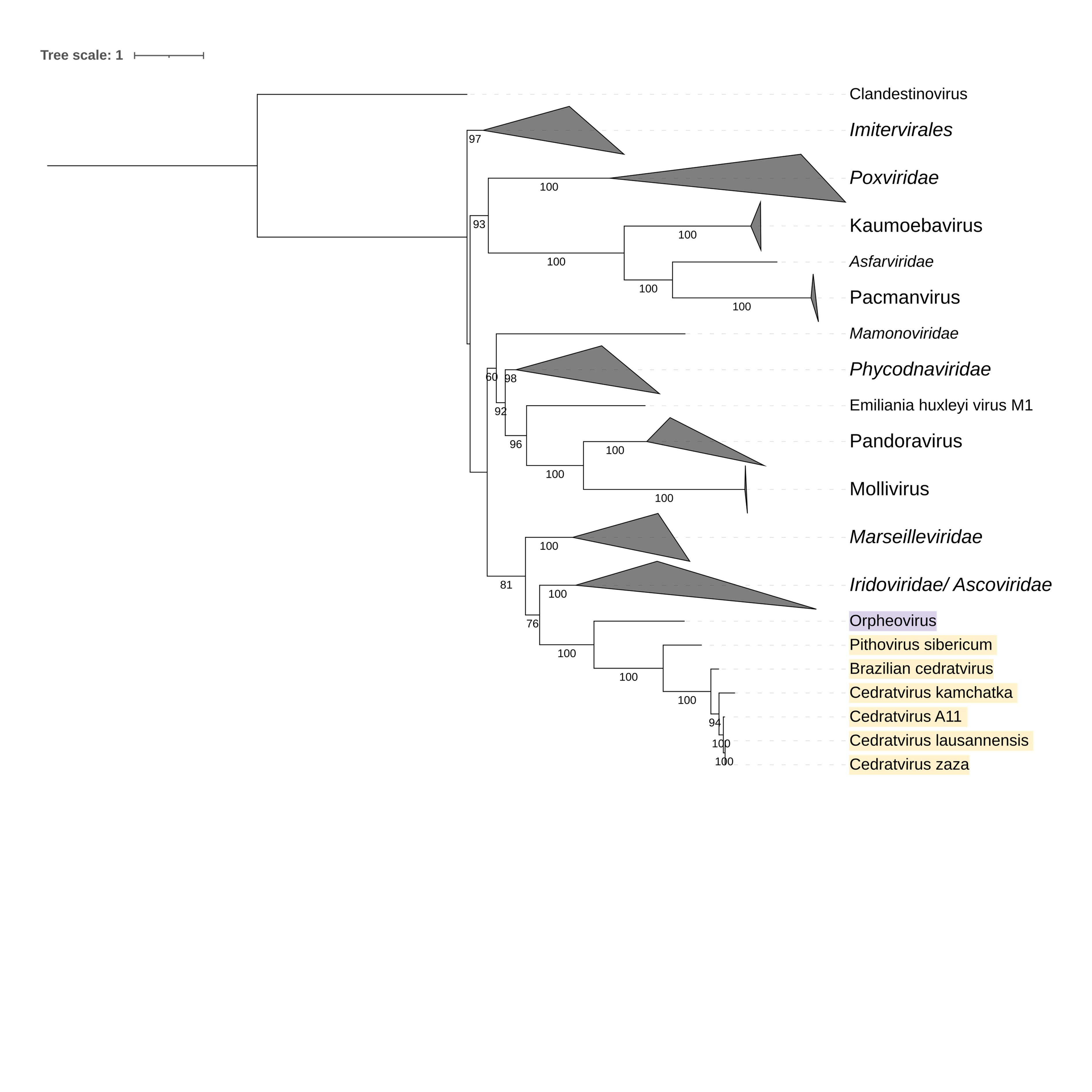
Supplementary figure 2 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of DNA polymerase family B gene present in the strict core genome with clandestinovirus (gene 1). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
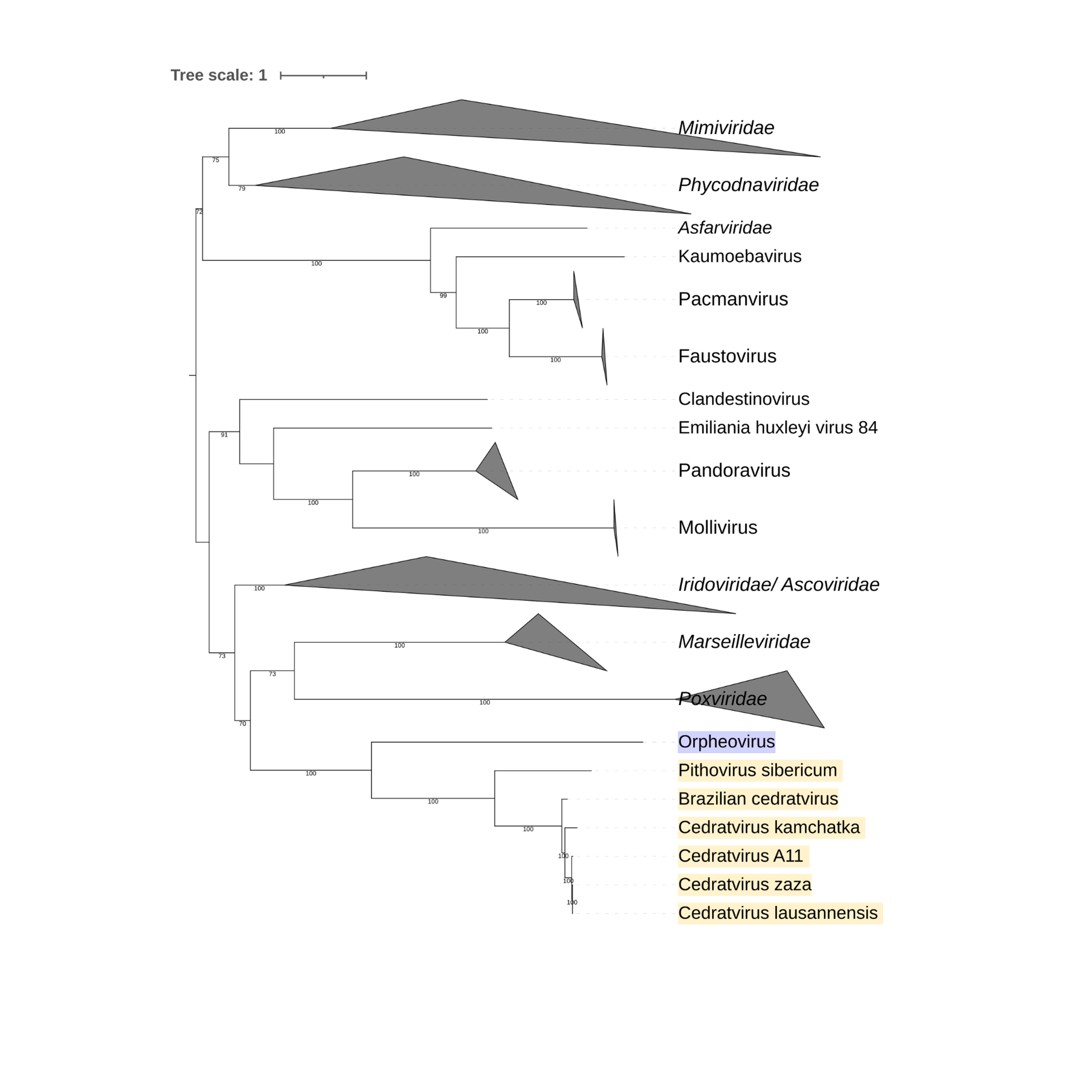
Supplementary figure 3 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of the DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB2 gene present in the strict core genome (gene 2). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
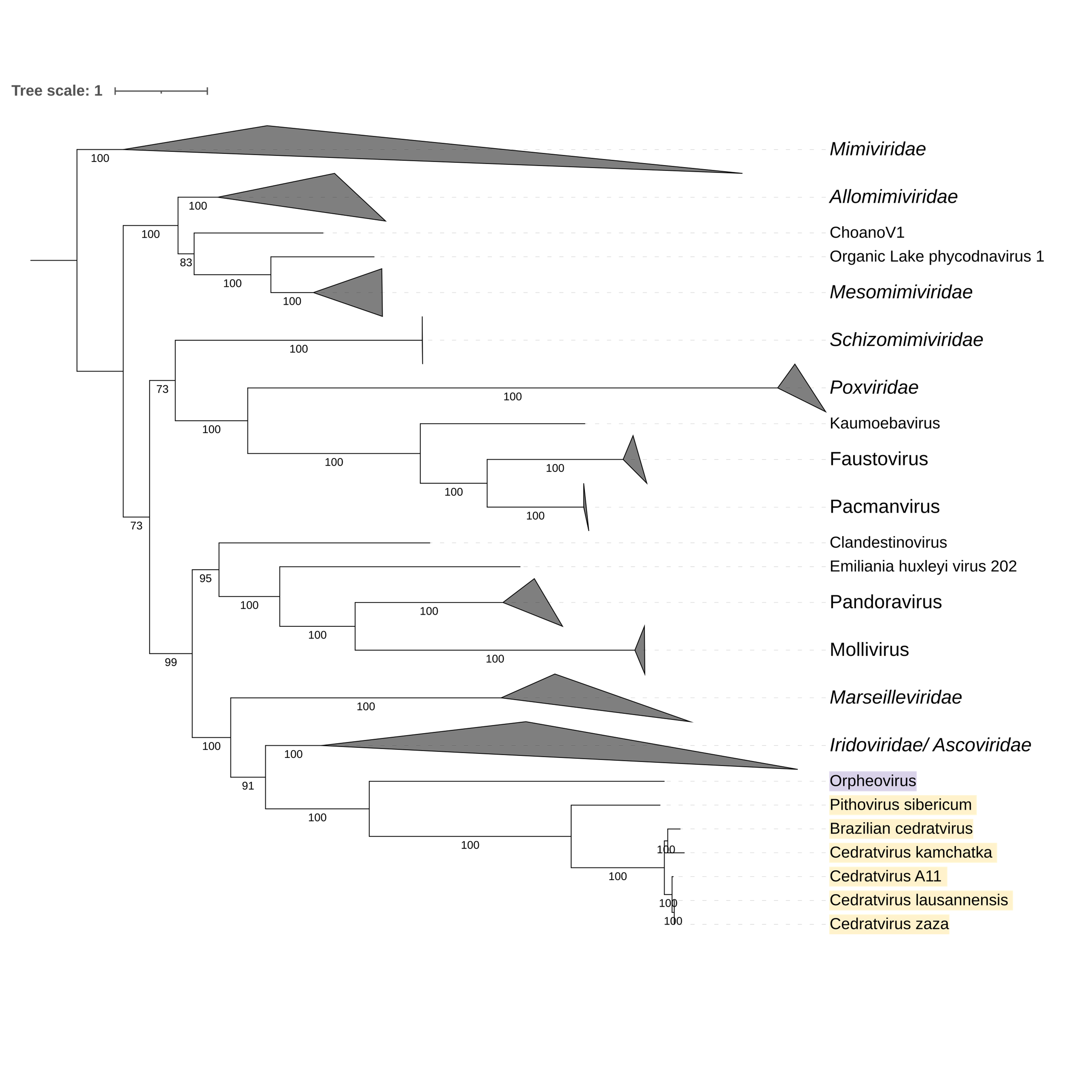
Supplementary figure 4 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of the DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1 gene present in the strict core genome (gene 3). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
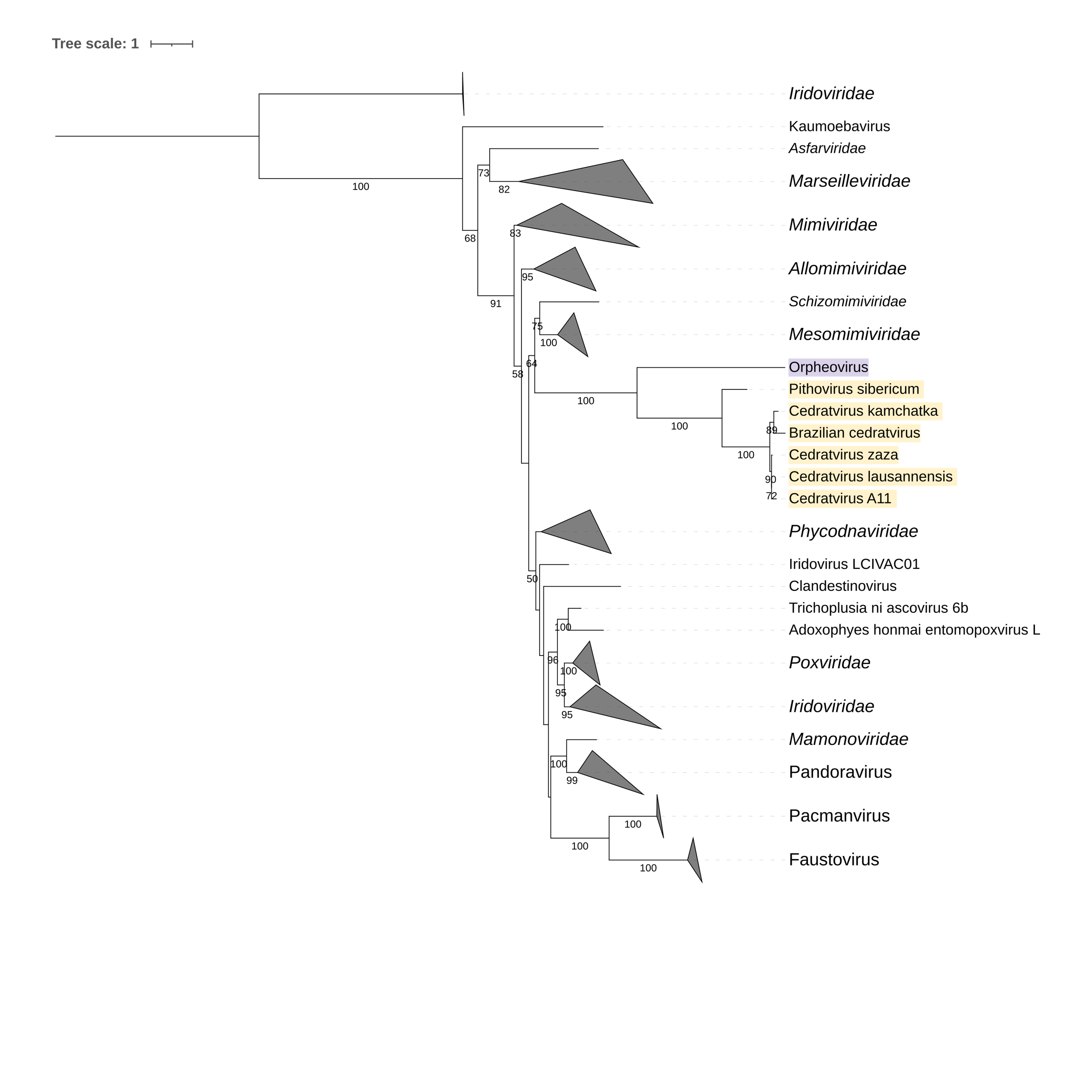
Supplementary figure 5 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of the Ribonucleotide reductase small subunit family gene present in the strict core genome (gene 4). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.

Supplementary figure 6 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of the Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase large subunit gene present in the strict core genome (gene 5). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >70 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
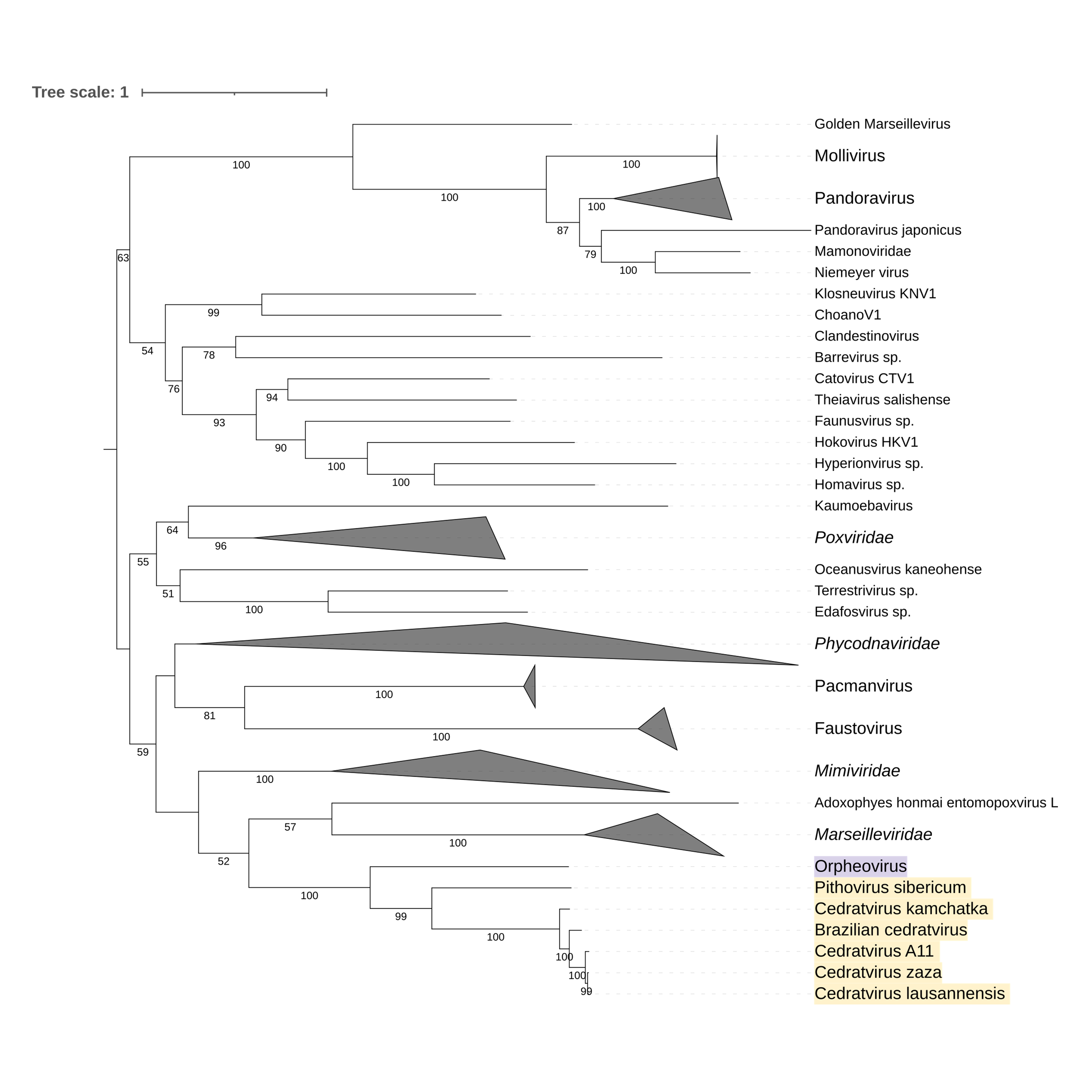
Supplementary figure 7 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of Nucleotide-binding protein kinase gene present in the strict core genome (gene 6). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.

Supplementary figure 8 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of Flap endonuclease-1 gene present in the strict core genome (gene 7). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >60 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
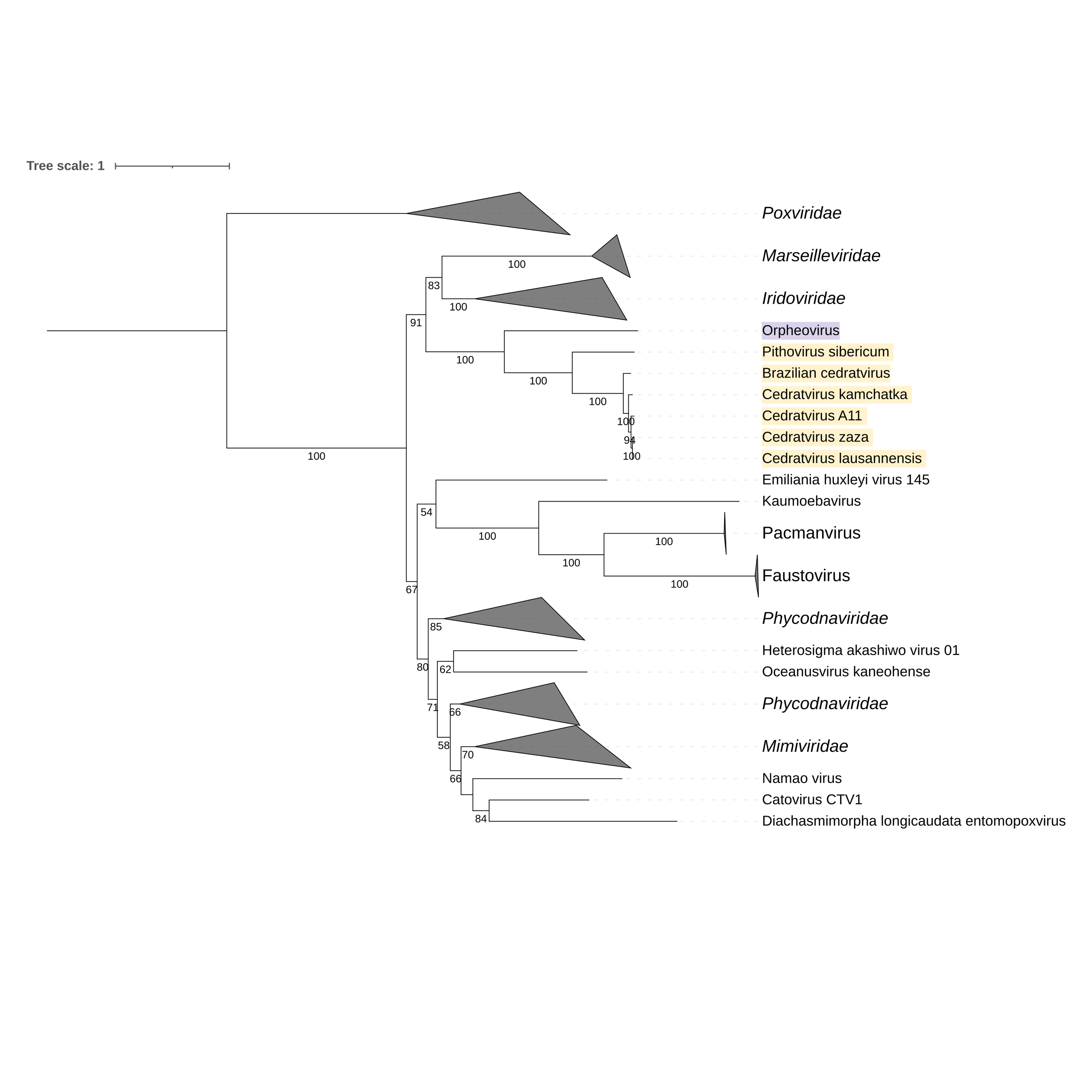
Supplementary figure 9 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of DNA topoisomerase IIA gene present in the strict core genome (gene 8). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
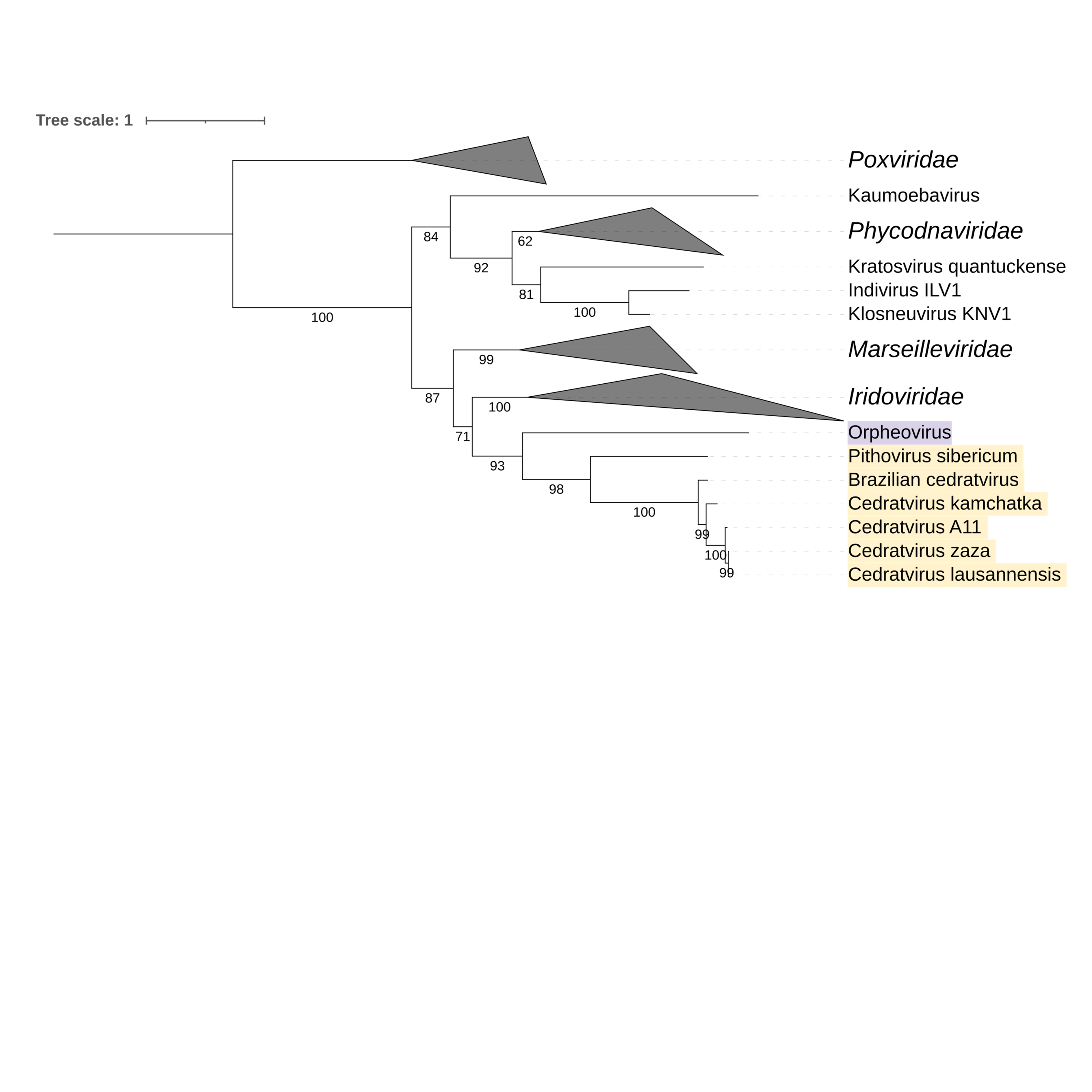
Supplementary figure 10 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of A18-like helicase gene present in the strict core genome (gene 10). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >60 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.

Supplementary figure 11 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of Transcription elongation factor TFIIS gene present in the strict core genome (gene 11). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.

Supplementary figure 12 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of Patatin-like phospholipase gene present in the strict core genome (gene 13). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.

Supplementary figure 13 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of D6-like helicase gene present in the strict core genome (gene 14). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >70 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
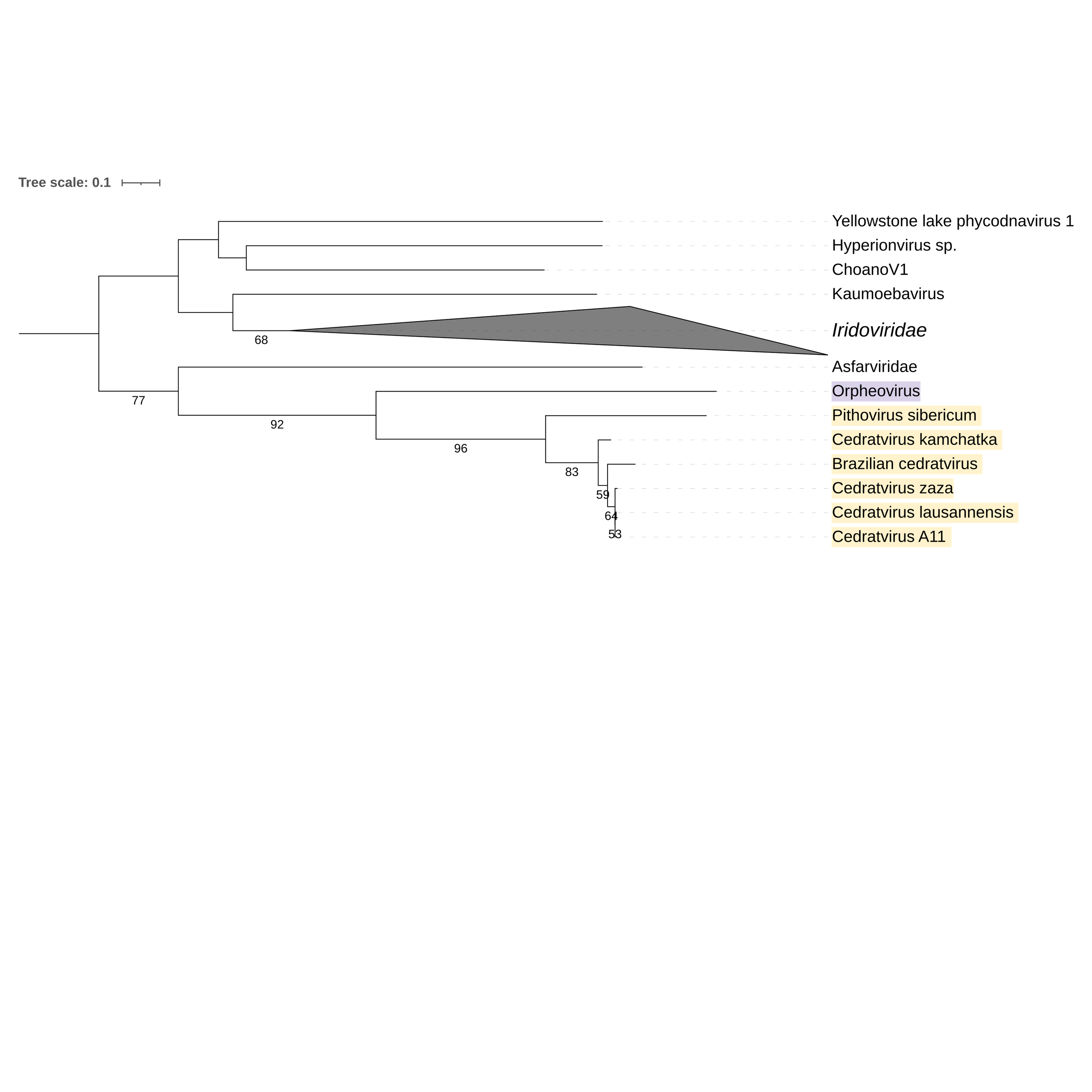
Supplementary figure 14 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of Sulfhydryl oxidase 1 gene present in the strict core genome (gene 15). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.

Supplementary figure 15 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of VSR Endonuclease gene present in the strict core genome (gene 16). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
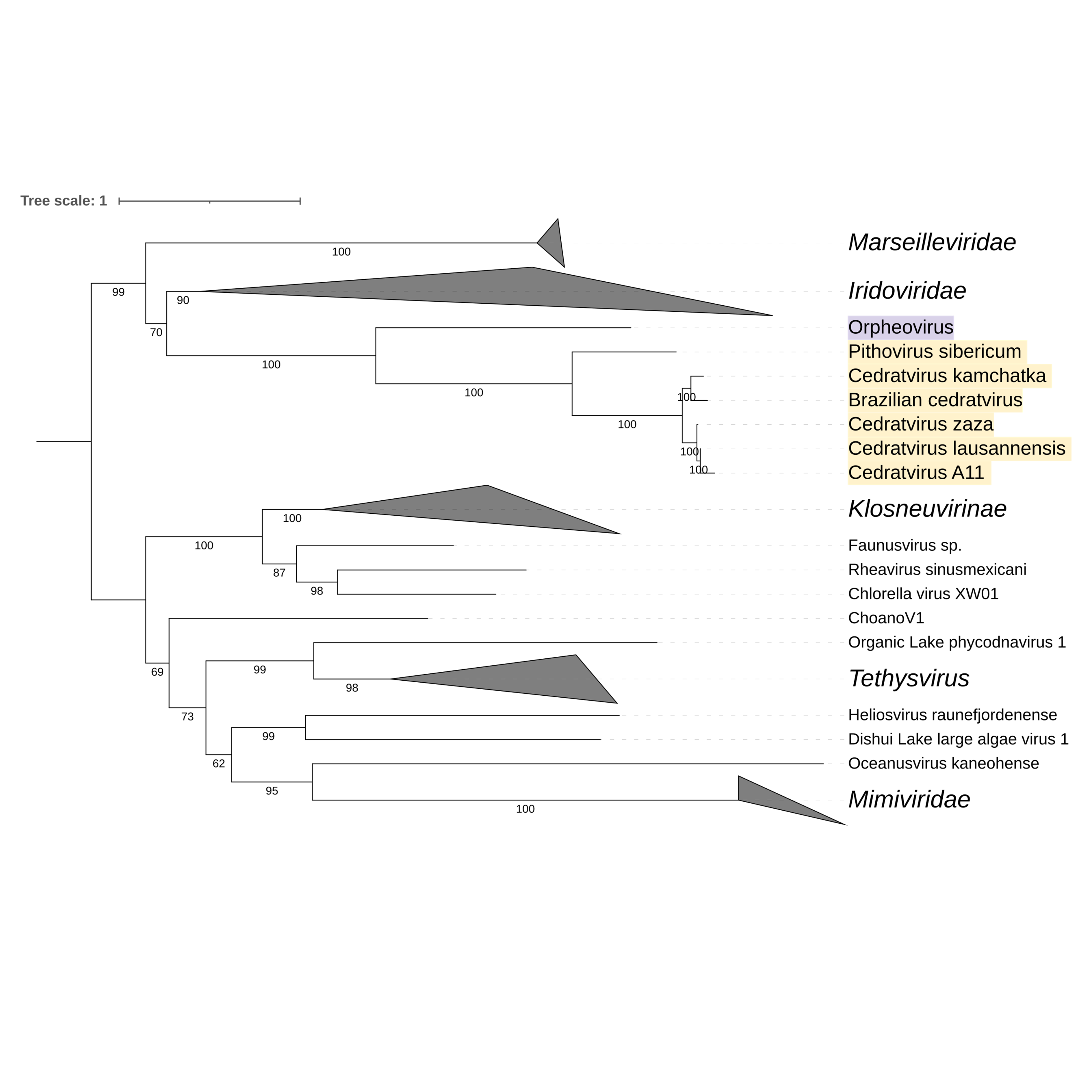
Supplementary figure 16 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of 5'-3' exoribonuclease gene present in the strict core genome (gene 17). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >60 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
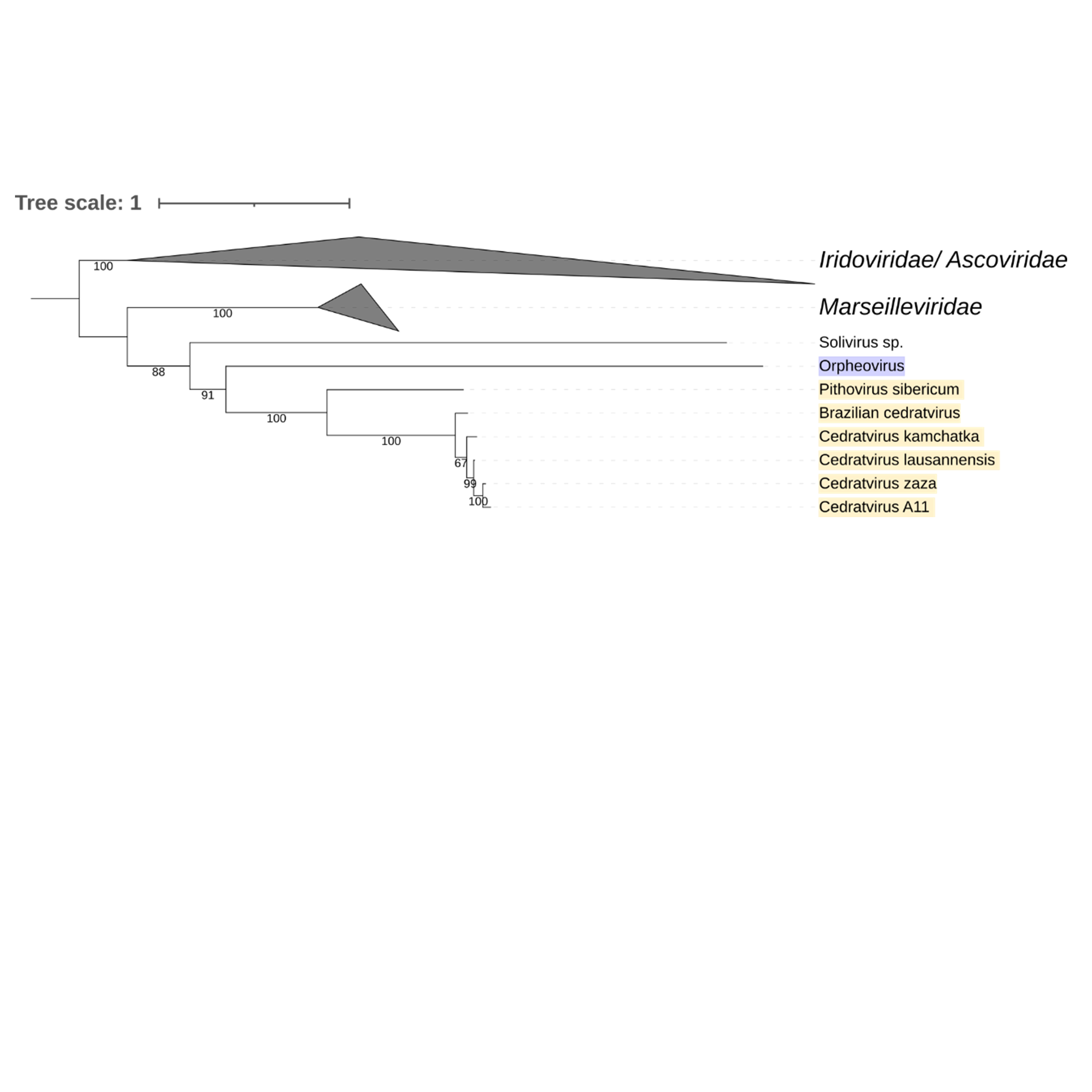
Supplementary figure 17 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of DNA repair exonuclease gene present in the strict core genome (gene 18). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >60 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
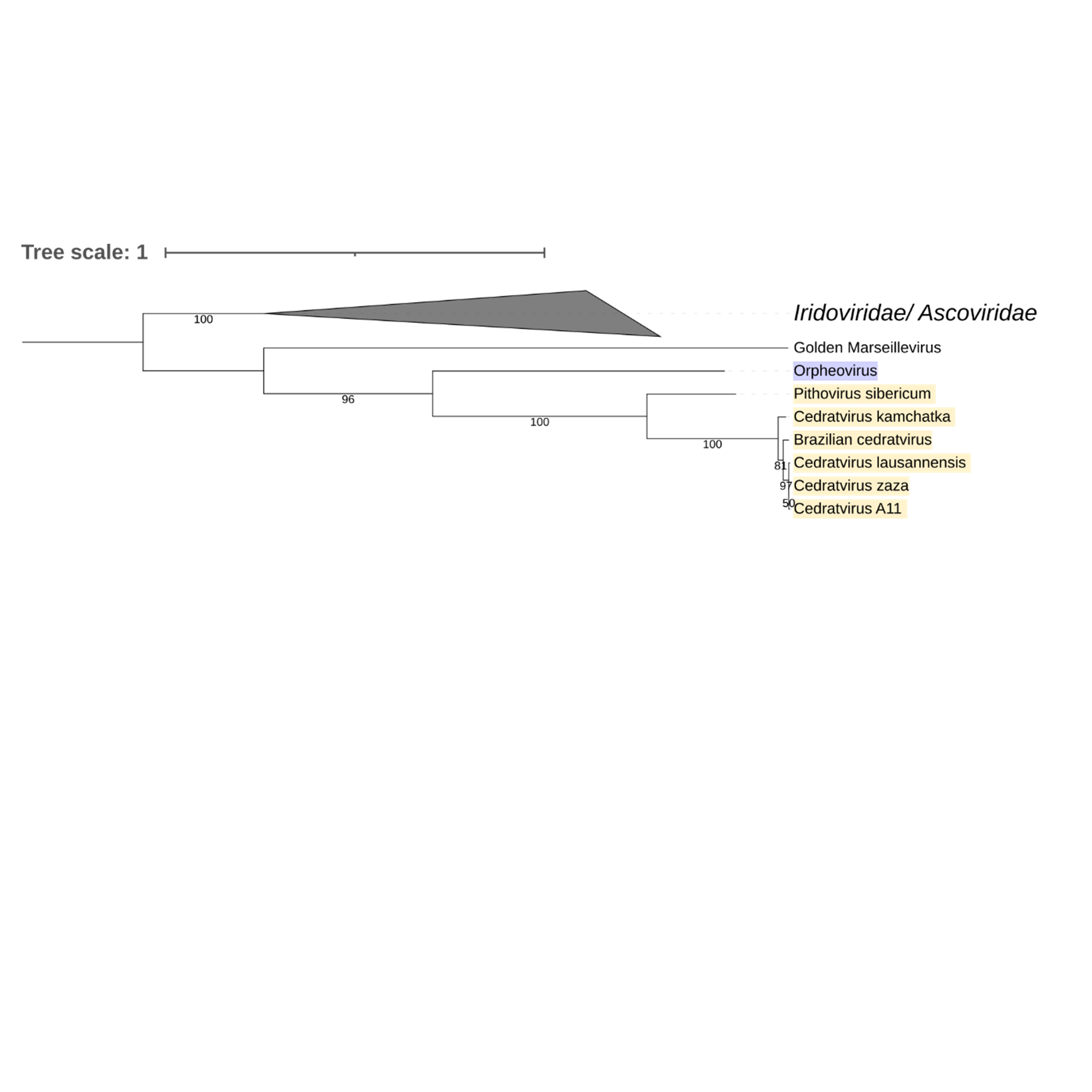
Supplementary figure 18 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of VLTF3 late transcription factor gene present in the strict core genome (gene 19). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.

Supplementary figure 19 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of ATP-dependent DNA ligase gene present in the strict core genome (gene 20). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >70 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
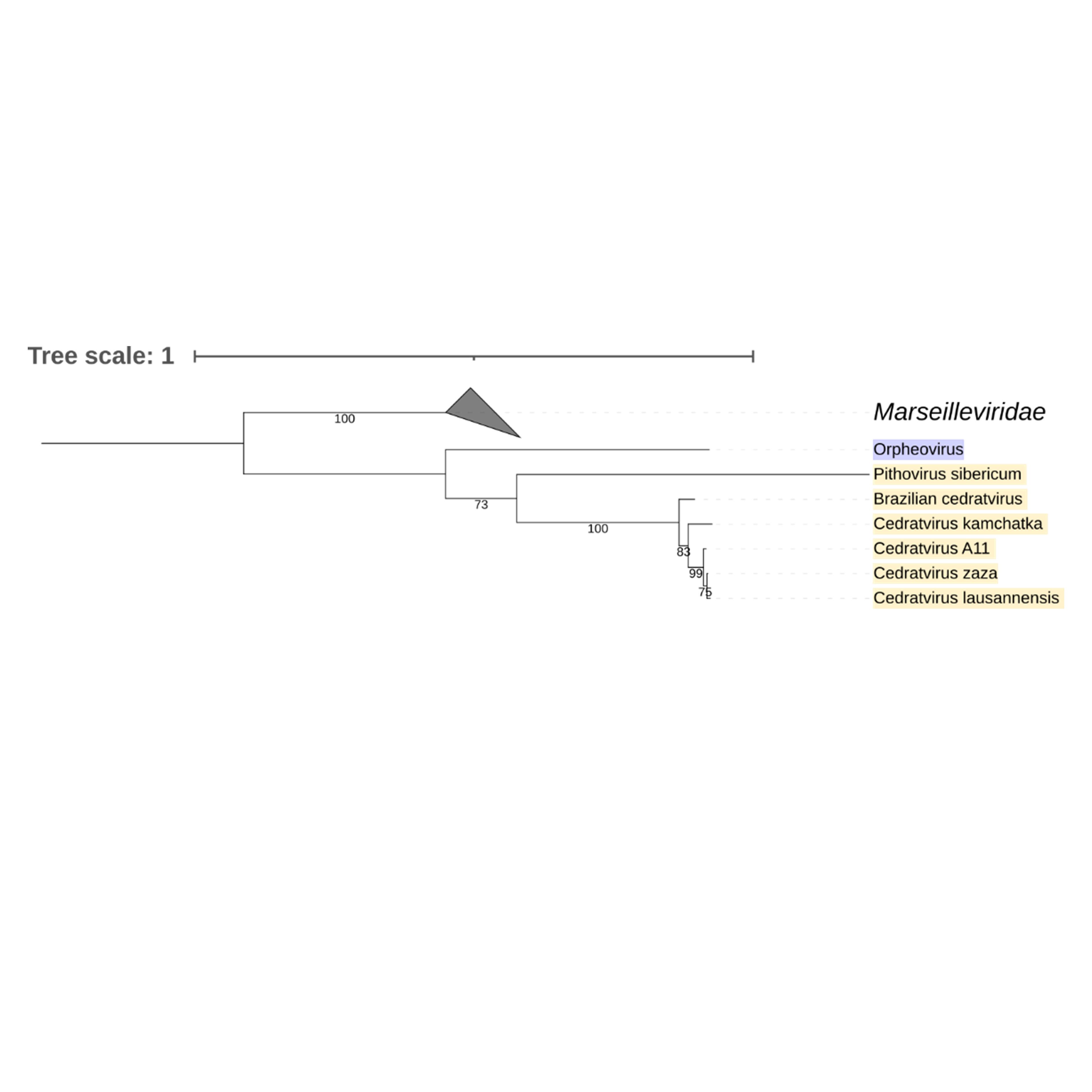
Supplementary figure 20 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of Hypothetical protein gene present in the strict core genome (gene 22). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >70 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
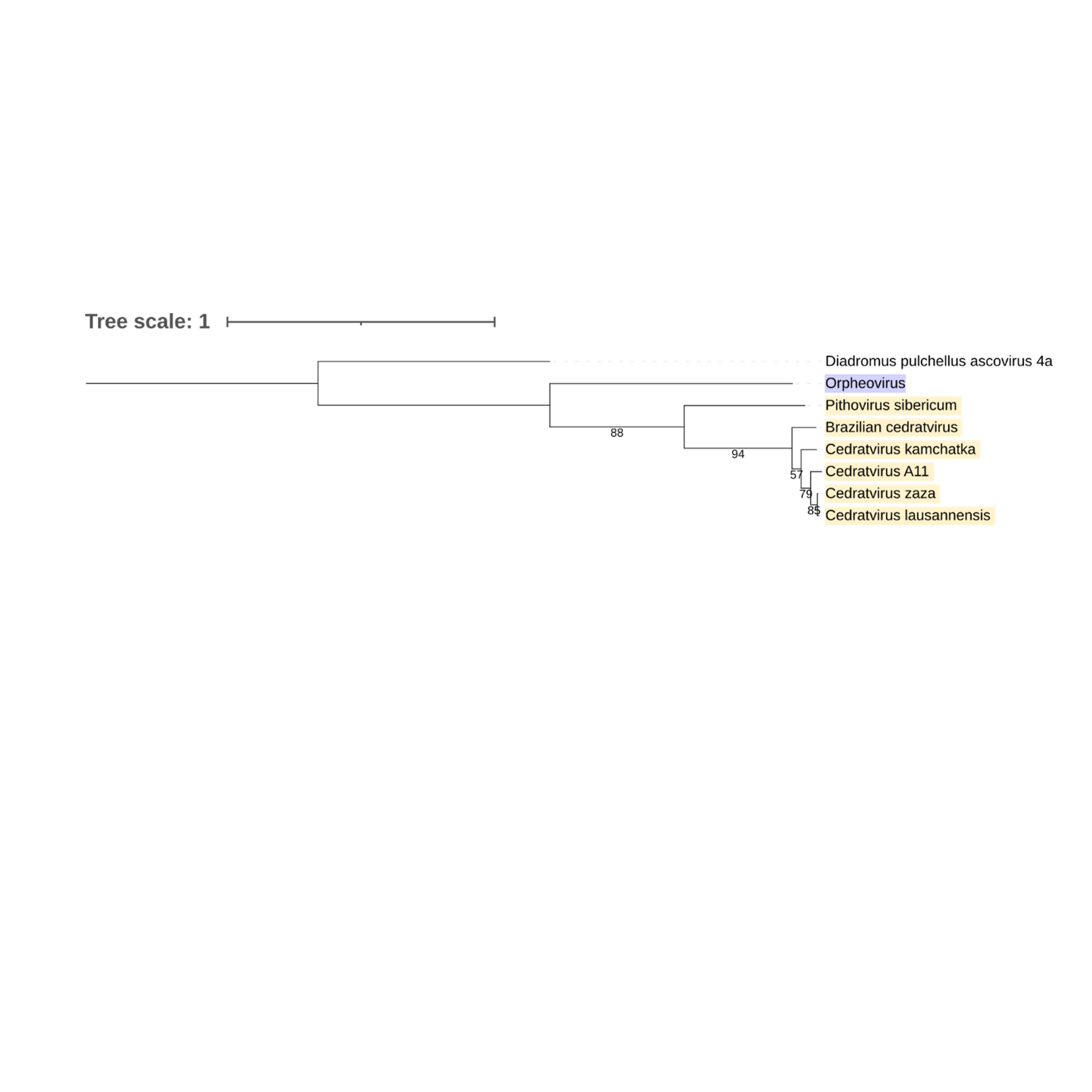
Supplementary figure 21 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences Hypothetical protein gene present in the strict core genome (gene 23). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
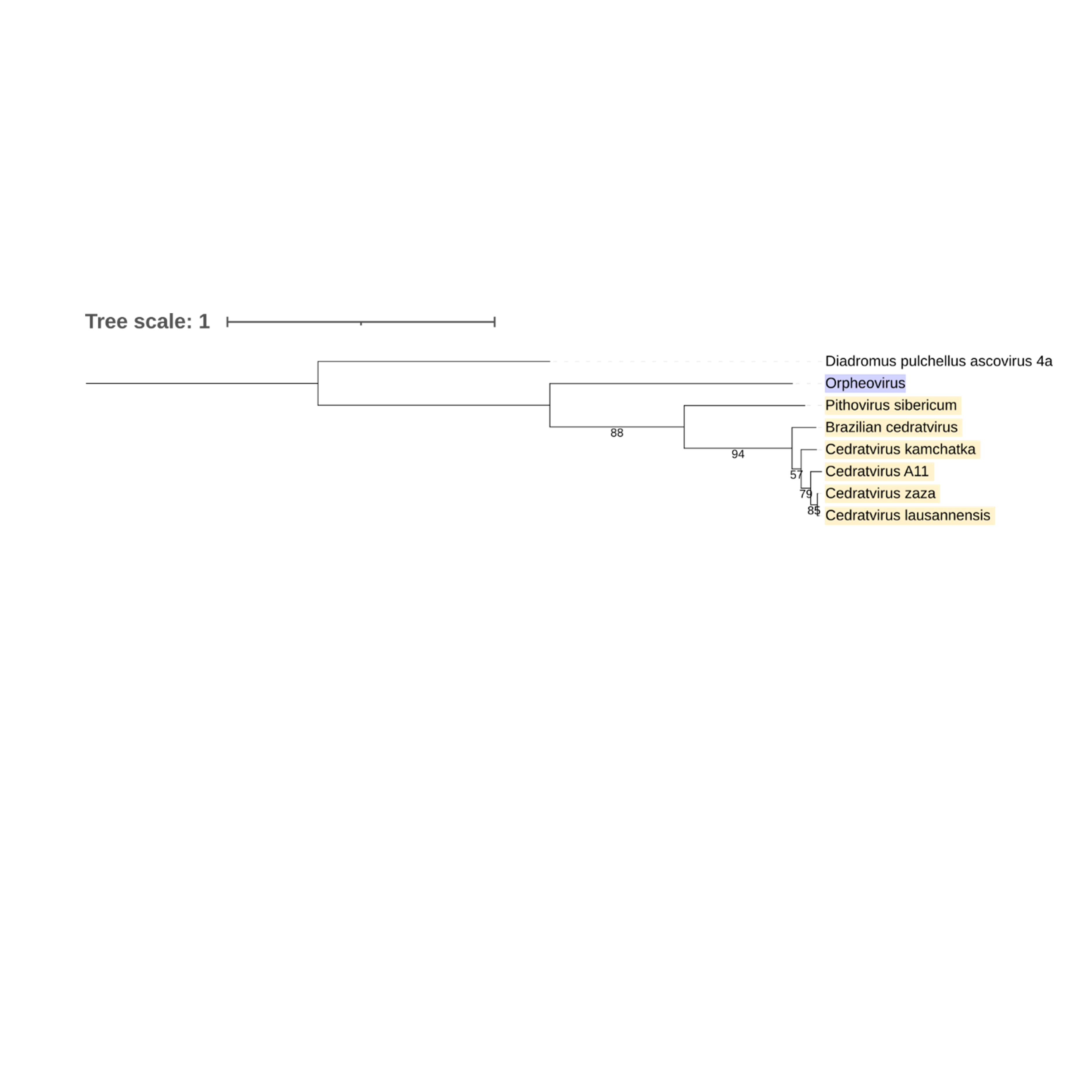
Supplementary figure 22 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of RNA Ligase gene present in the strict core genome (gene 24). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
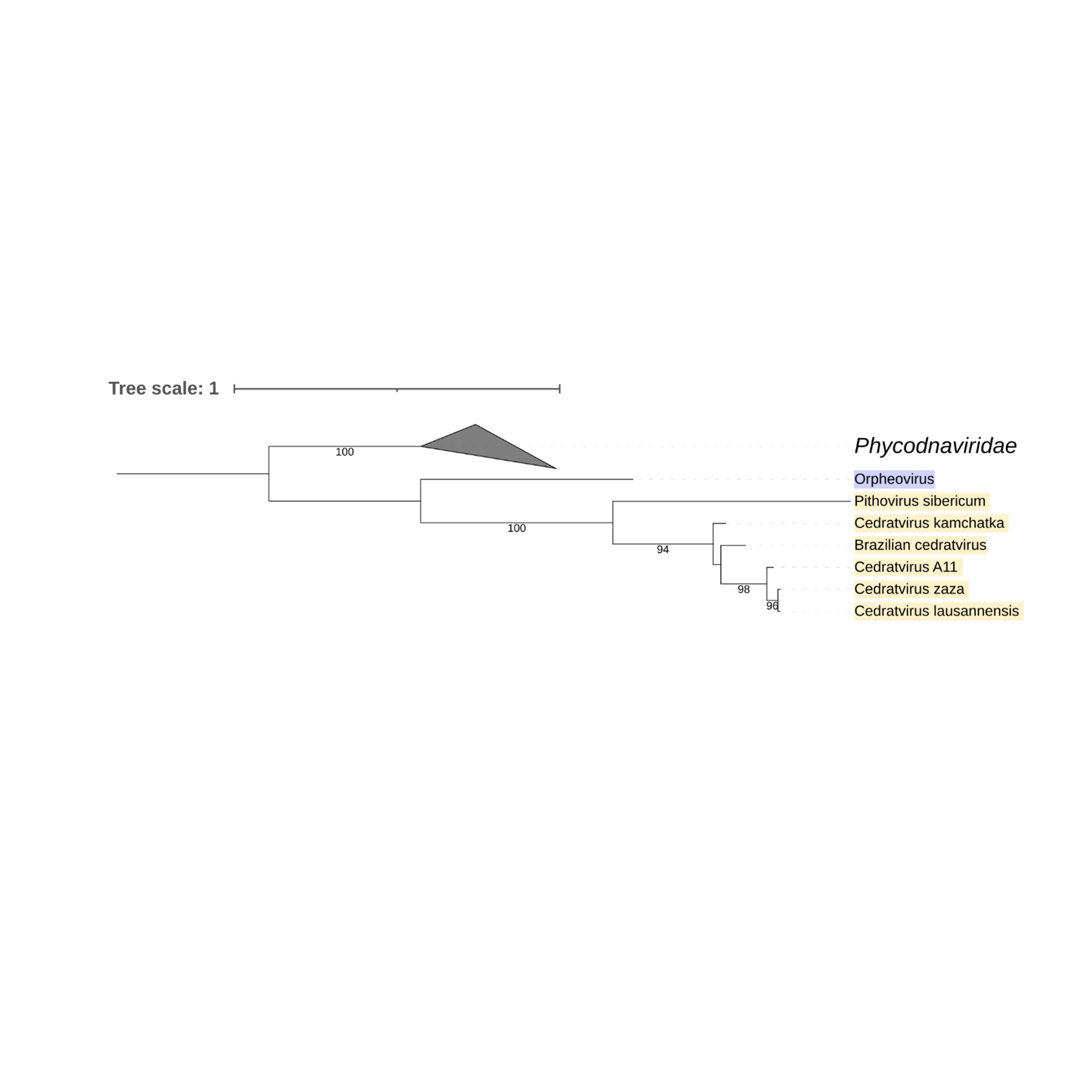
Supplementary figure 23 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of Thymidylate synthase gene present in the strict core genome (gene 25). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >90 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.

Supplementary figure 24 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences RNA Polymerase III gene present in the strict core genome (gene 26). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >70 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
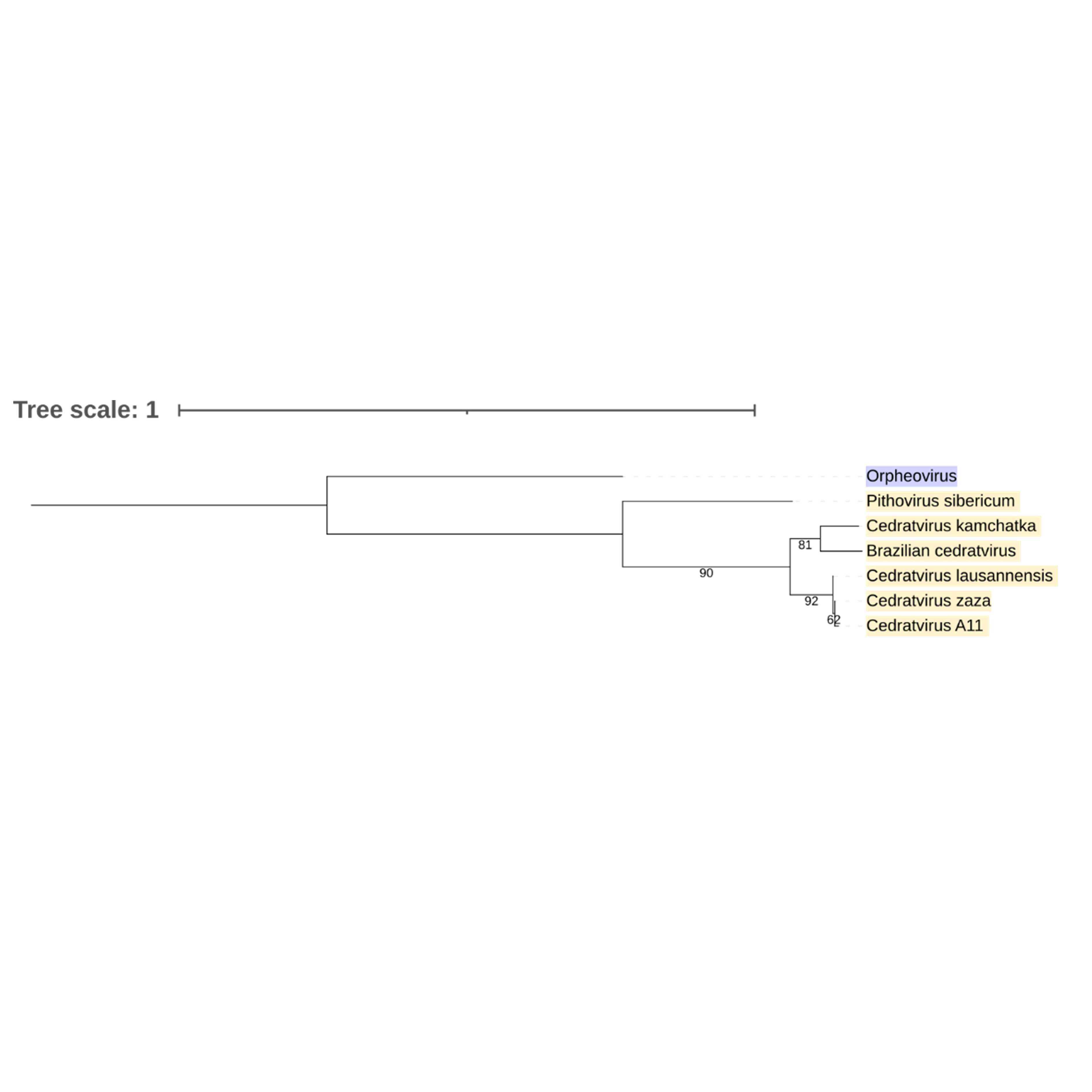
Supplementary figure 25 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of mRNA decapping complex subunit 2 gene present in the strict core genome (gene 27). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >60 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
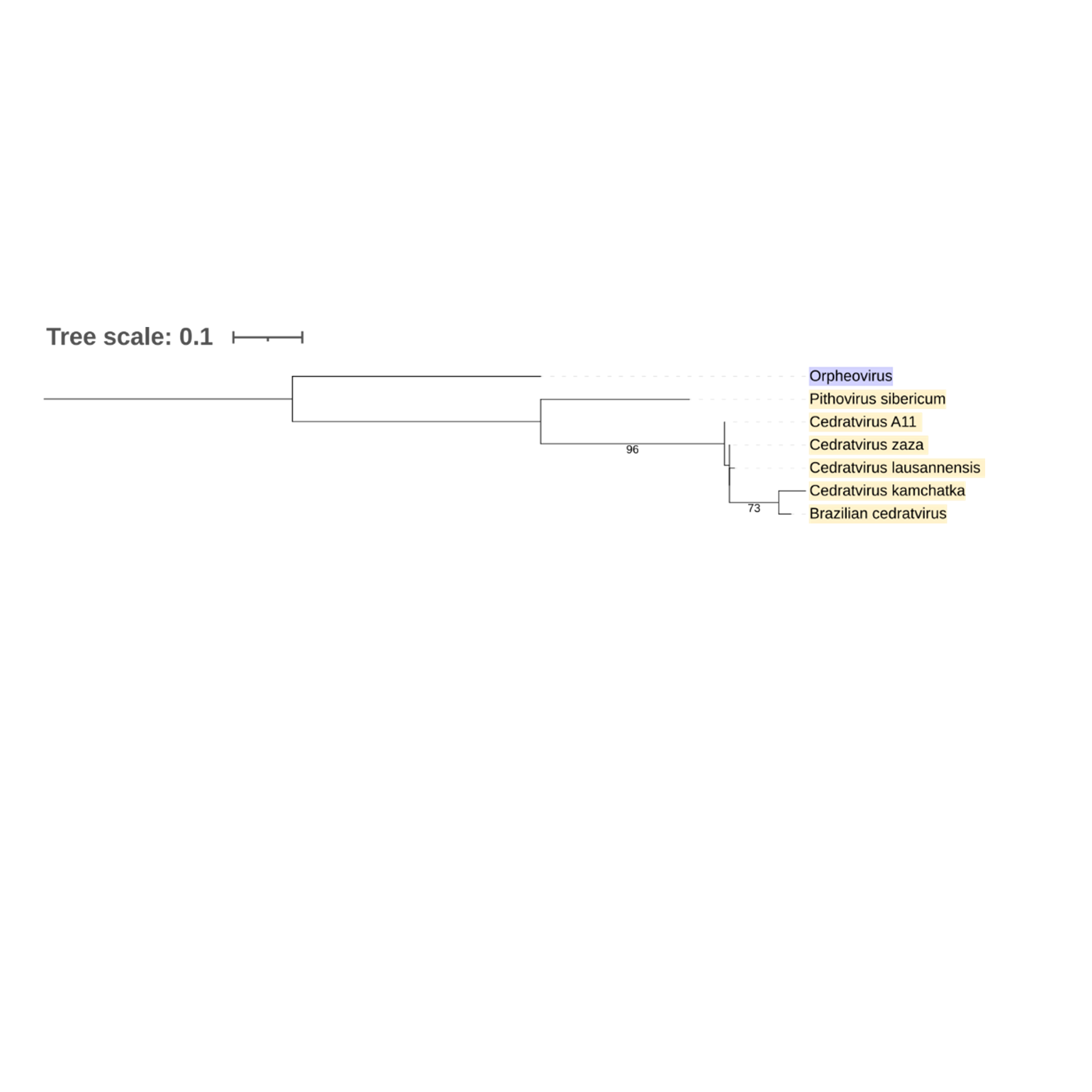
Supplementary figure 26 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of Transcription initiation factor gene present in the strict core genome (gene 28). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values 70 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
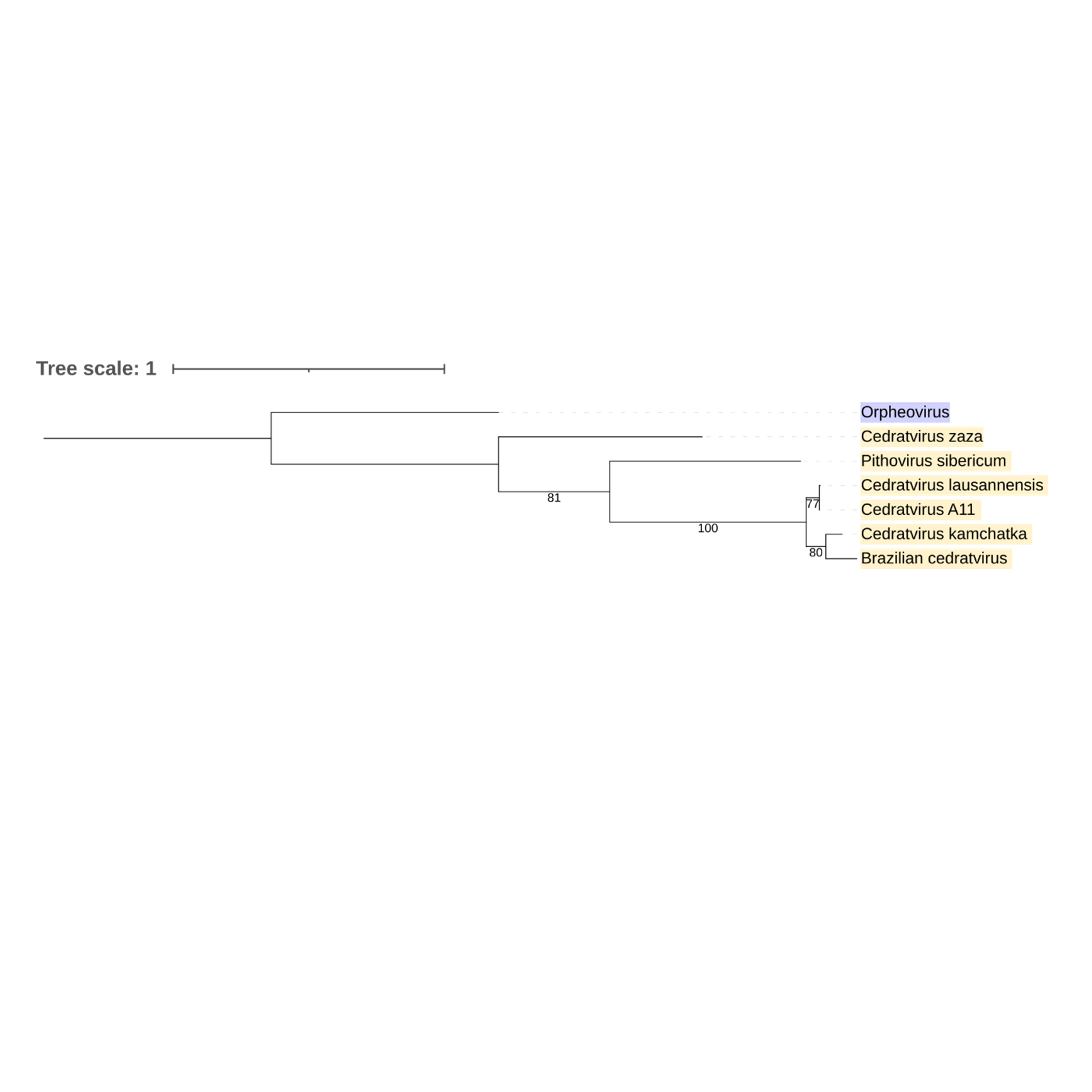
Supplementary figure 27 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of Hypothetical protein gene present in the strict core genome (gene 29). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >70 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.
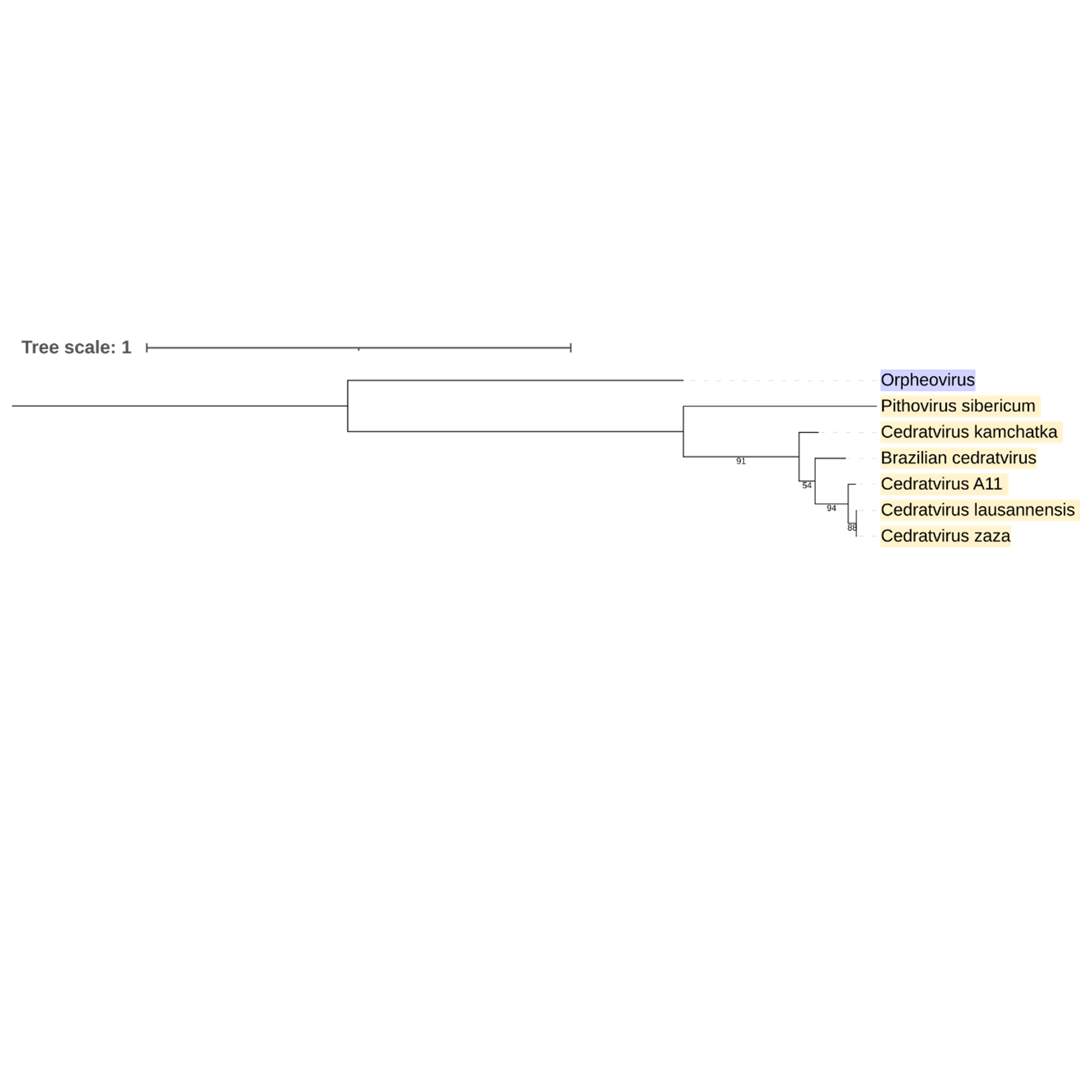
Supplementary figure 28 (above). Phylogeny of Nucleocytoviricota based on amino acid sequences of RNA polymerase II gene present in the strict core genome (gene 30). The bar indicates the rate of evolution. Only bootstrap values >50 are shown. Orpheovirus is colored in purple, pithovirus and cedratviruses are colored in yellow.


